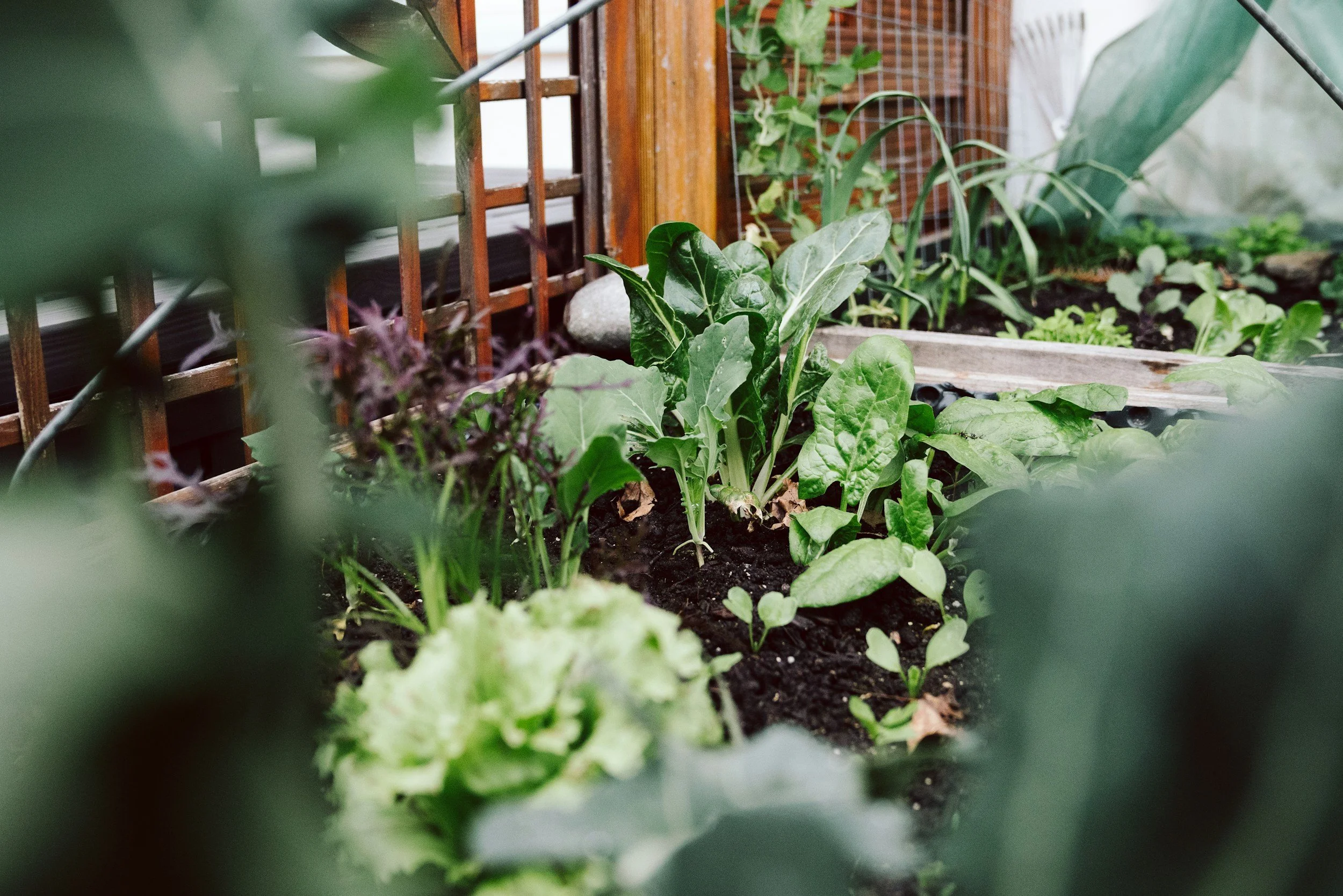
Planning a vegetable garden? Here's what to add to your soil in spring
/Soil quality is important when it comes to growing plants, particularly for food gardening. To ensure the optimal growth of edible crops, such as vegetables and fruits, it's important to enrich your soil with the relevant nutrients. In addition to nutrients, you'll need to ensure that your soil becomes a thriving ecosystem. One thing that inexperienced gardeners may forget is that the soil is a living organism; using organic and regenerative soil amendments can create the ideal conditions for your soil to foster an ecosystem that works to optimize conditions for your plants to thrive.
Healthy soil is living soil
Healthy, living soil aids in the decomposition of toxins, plays an essential role in root development, maintains the health of plant roots, enables the plant to take up and use nutrients effectively, strengthens the plant's immune defenses, and lessens the gardener's dependency on fertilizer and pesticides (including organic ones). Taking the time to amend your soil and prepare it for spring planting is essential for crops that are healthier not just for the consumer but also for the environment.
There are several ways to ensure that your soil is packed with everything it needs for optimal plant health and growth. This article shares some easy and inexpensive ways to amend your soil in the spring. Before adding anything to your soil, however, it's important to assess its current condition to determine exactly what it needs.
What is your soil like now?
Even if you've amended your soil in the past, its composition will change from one season to the next. One reason is because climatic conditions are continuously changing. Another reason soil may change is because the plants you've grown in it previously have used up essential nutrients. Unless you plant cover crops like sweet peas, oats, or hairy vetch in your soil when your regular growing season is over, your soil is likely to be deficient in one or more nutrients.
If you are growing food in the ground (and not in raised beds or containers), you should also be aware of what soil type you have. There are generally six types of soil: clay, sandy, peaty, chalky, silty, and loamy. Loamy soil is the kind that produces the best conditions for food gardening. Although it tends to be a little acidic, loamy soil has great structure, adequate drainage, holds moisture well, is full of nutrients, is easily to work with, and warms quickly, but doesn’t dry out quickly.
Do you need a soil test?
Although you can certainly grow fruit and vegetable plants in soil without testing it first, soil tests will enable you to create the best conditions for healthy crops that grow to their full potential and are able to resist many common plant diseases.
To get a better idea of the current condition of your soil, you'll want to perform a soil test. By testing the pH levels and nutrient composition, you'll be able to determine which amendments will best suit your soil's specific needs. Home testing kits are available at most garden centers, or you can send a sample off to a cooperative extension lab for more detailed results. Once you know what you're working with, you can give your soil the food it needs to create a balanced growing environment.
What is Soil Food?
Soil food is a term used to describe organic matter, such as compost and other amendments, that are added to soil to improve its structure and fertility. It typically includes materials like manure, green manures, mulches, rock dusts, seaweed extracts, fish emulsion and vermicompost. All of these components help build the soil's nutrient content and create an environment for beneficial organisms to thrive.
Below the surface, an incredible world of life buzzes with movement as microscopic creatures and tiny organisms traverse the soil in search of the perfect living space. They consume soil, excrete nutrients into it and contribute to its fertility, making it suitable for growing crops. They facilitate the conversion of natural minerals into a form that increases soil productivity.
If you are contemplating maintaining a food garden for the long term, then you need to invest significantly in soil food. Soil food is comprised of a diverse community of organisms. These organisms vary in sizes. They may be single-celled algae, fungi, bacteria, protozoa, nematodes, or arthropods. They can also be beneficial insects, earthworms, or even vertebrates.
Adding amendments
Adding organic material to your soil is one of the best ways to provide it with food that will nourish it for optimal growth. Organic material is generally composed of decaying plant or animal material, and it helps improve soil structure, provides nutrients, and increases water-holding capacity. Compost, well-rotted manure, leaf mold, grass clippings, and straw are all great sources of organic matter.
In addition to organic material, there are several other amendments that can help improve your soil's health and fertility, depending on its needs. Gypsum helps break up clay particles, allowing for better drainage and root penetration. Lime helps raise pH levels in acidic soils, making them more suitable for growing food crops. Rock dusts provide an array of trace minerals, while fish emulsion and seaweed extracts help provide nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorus.
Adding organic material to your soil in spring thus helps create the ideal growing conditions: it helps your soil retain moisture, reducing the need for frequent watering. It also helps reduce compaction and improves drainage, both of which are important for the healthy growth of plant roots. Additionally, organic material releases essential minerals that plants need to survive and thrive. As organic matter breaks down in the soil, it provides food for the microorganisms living there—the more microorganisms, the healthier your soil will be.
like this? Please pin!
The various organisms that are used to augment the fertility of soil can also help prevent soil pollution by decomposing organic compounds, insecticides, and pesticides, and thus help deter them from entering into the water supply. Thus, a healthy soil biology is also crucial for the maintaining the natural landscape of a place. If the natural landscape is kept healthy, it helps to benefit the surrounding environment.
Your garden is only as good as your soil
The health of your soil is the foundation of a successful vegetable garden. By testing your soil and adding the right amendments in springtime, you can give it the food it needs to create a balanced growing environment. With a nutrient-rich soil, you will have healthy plants that can resist pests and diseases, as well as produce a bountiful harvest of delicious fruits and vegetables.
With the right soil supplements, you can make your soil bloom and enjoy an abundance of crop yields. Using the right soil food can help to improve the fertility of your garden soil, allowing both professional and amateur gardeners to increase their yield and enhance its quality.
Want to find out more about how to amend your soil and grow a healthy, abundant food garden? Sign up for our free online course, The Art of Food Gardening, by clicking the button in the image above and create your own food paradise in 2 weeks or less!